| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Securing the Network in Oracle Solaris 11.1 Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Securing the Network in Oracle Solaris 11.1 Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
1. Using Link Protection in Virtualized Environments
2. Tuning Your Network (Tasks)
3. Web Servers and the Secure Sockets Layer Protocol
4. IP Filter in Oracle Solaris (Overview)
Information Sources for Open Source IP Filter
Guidelines for Using IP Filter
Using IP Filter Configuration Files
Using IP Filter's Packet Filtering Feature
Configuring Packet Filtering Rules
Using IP Filter's Address Pools Feature
6. IP Security Architecture (Overview)
8. IP Security Architecture (Reference)
9. Internet Key Exchange (Overview)
IP Filter executes a sequence of steps as a packet is processed. The following diagram illustrates the steps of packet processing and how filtering integrates with the TCP/IP protocol stack.
Figure 4-1 Packet Processing Sequence
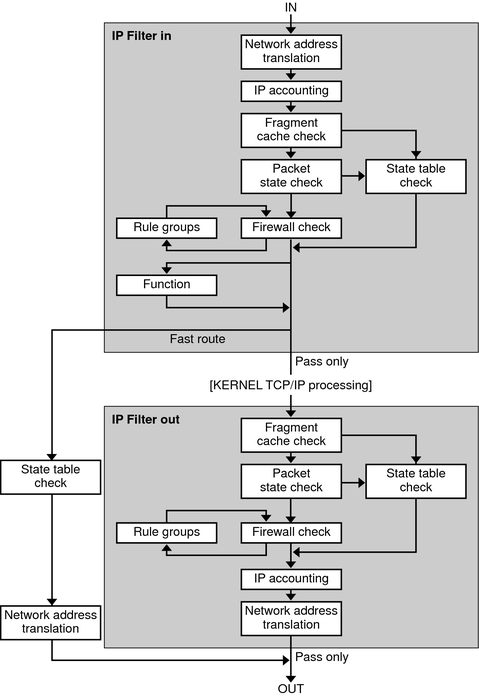
The packet processing sequence includes the following:
Network Address Translation (NAT)
The translation of a private IP address to a different public address, or the aliasing of multiple private addresses to a single public one. NAT allows an organization to resolve the problem of IP address depletion when the organization has existing networks and needs to access the Internet.
IP Accounting
Input and output rules can be separately set up, recording the number of bytes that pass through. Each time a rule match occurs, the byte count of the packet is added to the rule and allows for collection of cascading statistics.
Fragment Cache Check
By default, fragmented packets are cached. When the all fragments for a specific packet arrive, the filtering rules are applied and either the fragments are allowed or blocked. If set defrag off appears in the rules file, then fragments are not cached.
Packet State Check
If keep state is included in a rule, all packets in a specified session are passed or blocked automatically, depending on whether the rule says pass or block.
Firewall Check
Input and output rules can be separately set up, determining whether or not a packet will be allowed through IP Filter, into the kernel's TCP/IP routines, or out onto the network.
Groups
Groups allow you to write your rule set in a tree fashion.
Function
A function is the action to be taken. Possible functions include block, pass, literal, and send ICMP response.
Fast-route
Fast-route signals IP Filter to not pass the packet into the UNIX IP stack for routing, which results in a TTL decrement.
IP Authentication
Packets that are authenticated are only passed through the firewall loops once to prevent double-processing.