| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Securing the Network in Oracle Solaris 11.1 Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
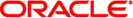
|
Securing the Network in Oracle Solaris 11.1 Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
1. Using Link Protection in Virtualized Environments
2. Tuning Your Network (Tasks)
3. Web Servers and the Secure Sockets Layer Protocol
4. IP Filter in Oracle Solaris (Overview)
6. IP Security Architecture (Overview)
Encapsulating Security Payload
Security Considerations When Using AH and ESP
Authentication and Encryption Algorithms in IPsec
Authentication Algorithms in IPsec
Encryption Algorithms in IPsec
Transport and Tunnel Modes in IPsec
Virtual Private Networks and IPsec
IPsec and Oracle Solaris Zones
8. IP Security Architecture (Reference)
9. Internet Key Exchange (Overview)
Figure 6-1 shows how an IP addressed packet, as part of an IP datagram, proceeds when IPsec has been invoked on an outbound packet. The flow diagram illustrates where authentication header (AH) and encapsulating security payload (ESP) entities can be applied to the packet. How to apply these entities, as well as how to choose the algorithms, are described in subsequent sections.
Figure 6-2 shows the IPsec inbound process.
Figure 6-1 IPsec Applied to Outbound Packet Process
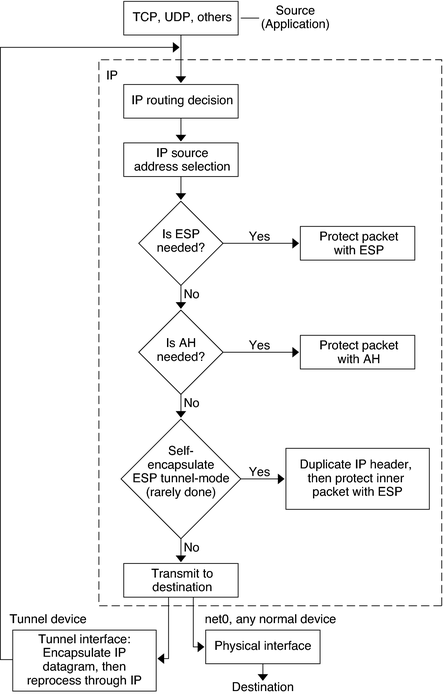
Figure 6-2 IPsec Applied to Inbound Packet Process