| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |

|
Oracle Solaris 11.1 Administration: Security Services Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |

|
Oracle Solaris 11.1 Administration: Security Services Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
1. Security Services (Overview)
Part II System, File, and Device Security
2. Managing Machine Security (Overview)
3. Controlling Access to Systems (Tasks)
4. Virus Scanning Service (Tasks)
5. Controlling Access to Devices (Tasks)
6. Verifying File Integrity by Using BART (Tasks)
7. Controlling Access to Files (Tasks)
Part III Roles, Rights Profiles, and Privileges
8. Using Roles and Privileges (Overview)
9. Using Role-Based Access Control (Tasks)
10. Security Attributes in Oracle Solaris (Reference)
Part IV Cryptographic Services
11. Cryptographic Framework (Overview)
12. Cryptographic Framework (Tasks)
Part V Authentication Services and Secure Communication
14. Using Pluggable Authentication Modules
17. Using Simple Authentication and Security Layer
18. Network Services Authentication (Tasks)
19. Introduction to the Kerberos Service
20. Planning for the Kerberos Service
21. Configuring the Kerberos Service (Tasks)
22. Kerberos Error Messages and Troubleshooting
23. Administering Kerberos Principals and Policies (Tasks)
Ways to Administer Kerberos Principals and Policies
Command-Line Equivalents of the SEAM Tool
The Only File Modified by the SEAM Tool
Print and Online Help Features of the SEAM Tool
Working With Large Lists in the SEAM Tool
Administering Kerberos Principals
Administering Kerberos Principals (Task Map)
Automating the Creation of New Kerberos Principals
How to View the List of Kerberos Principals
How to View a Kerberos Principal's Attributes
How to Create a New Kerberos Principal
How to Duplicate a Kerberos Principal
How to Modify a Kerberos Principal
How to Delete a Kerberos Principal
How to Set Up Defaults for Creating New Kerberos Principals
How to Modify the Kerberos Administration Privileges
Administering Kerberos Policies
Administering Kerberos Policies (Task Map)
How to View the List of Kerberos Policies
How to View a Kerberos Policy's Attributes
How to Create a New Kerberos Policy
How to Duplicate a Kerberos Policy
Using the SEAM Tool With Limited Kerberos Administration Privileges
Administering Keytab Files (Task Map)
How to Add a Kerberos Service Principal to a Keytab File
How to Remove a Service Principal From a Keytab File
How to Display the Keylist (Principals) in a Keytab File
How to Temporarily Disable Authentication for a Service on a Host
24. Using Kerberos Applications (Tasks)
25. The Kerberos Service (Reference)
This section provides step-by-step instructions used to administer policies with the SEAM Tool. This section also provides examples of command-line equivalents, when available.
|
An example of the command-line equivalent follows this procedure.
See How to Start the SEAM Tool for more information.
$ /usr/sbin/gkadmin
The list of policies is displayed.
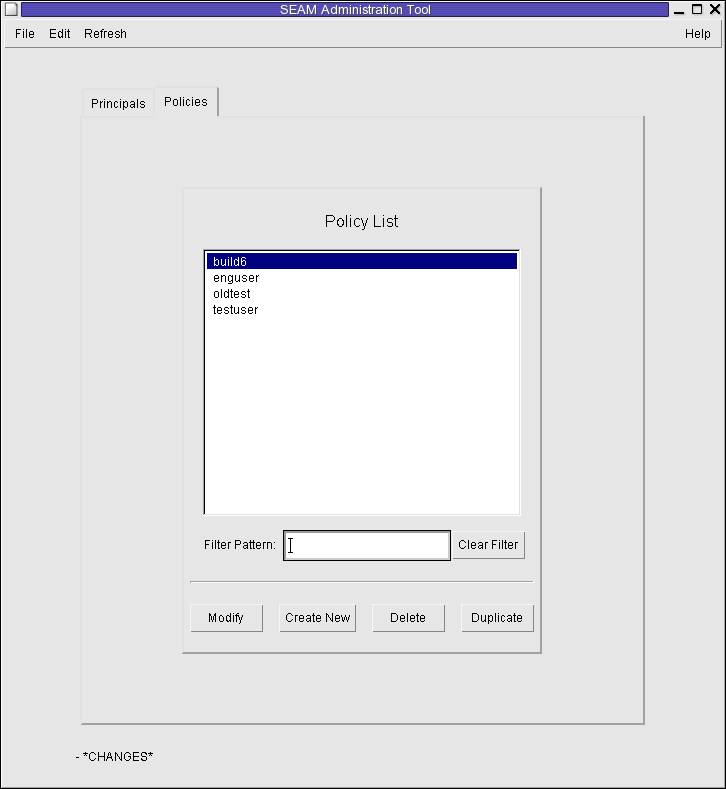
Type a filter string in the Filter field, and press Return. If the filter succeeds, the list of policies that match the filter is displayed.
The filter string must consist of one or more characters. Because the filter mechanism is case sensitive, you need to use the appropriate uppercase and lowercase letters for the filter. For example, if you type the filter string ge, the filter mechanism displays only the policies with the ge string in them (for example, george or edge).
If you want to display the entire list of policies, click Clear Filter.
Example 23-9 Viewing the List of Kerberos Policies (Command Line)
In the following example, the list_policies command of kadmin is used to list all the policies that match *user*. Wildcards can be used with the list_policies command.
kadmin: list_policies *user* testuser enguser kadmin: quit
An example of the command-line equivalent follows this procedure.
See How to Start the SEAM Tool for more information.
$ /usr/sbin/gkadmin
The Policy Details panel is displayed.
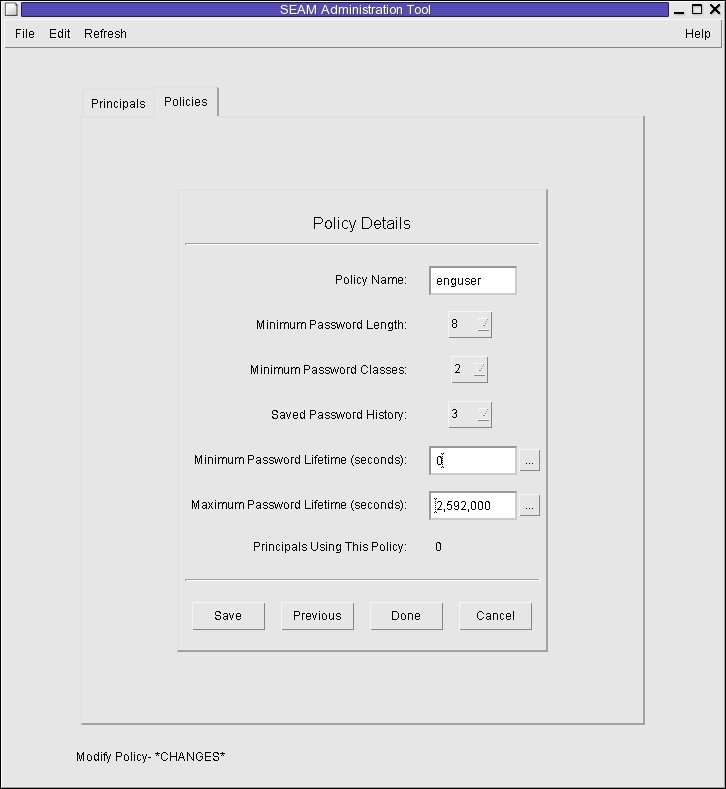
Example 23-10 Viewing a Kerberos Policy's Attributes
The following example shows the Policy Details panel when you are viewing the test policy.
Example 23-11 Viewing a Kerberos Policy's Attributes (Command Line)
In the following example, the get_policy command of kadmin is used to view the attributes of the enguser policy.
kadmin: get_policy enguser Policy: enguser Maximum password life: 2592000 Minimum password life: 0 Minimum password length: 8 Minimum number of password character classes: 2 Number of old keys kept: 3 Reference count: 0 kadmin: quit
The Reference count is the number of principals that use this policy.
An example of the command-line equivalent follows this procedure.
See How to Start the SEAM Tool for more information.
$ /usr/sbin/gkadmin
The Policy Details panel is displayed.
The policy name is mandatory.
Choose Context-Sensitive Help from the Help menu for information about the various attributes in this window. Or, go to Table 23-5 for all the policy attribute descriptions.
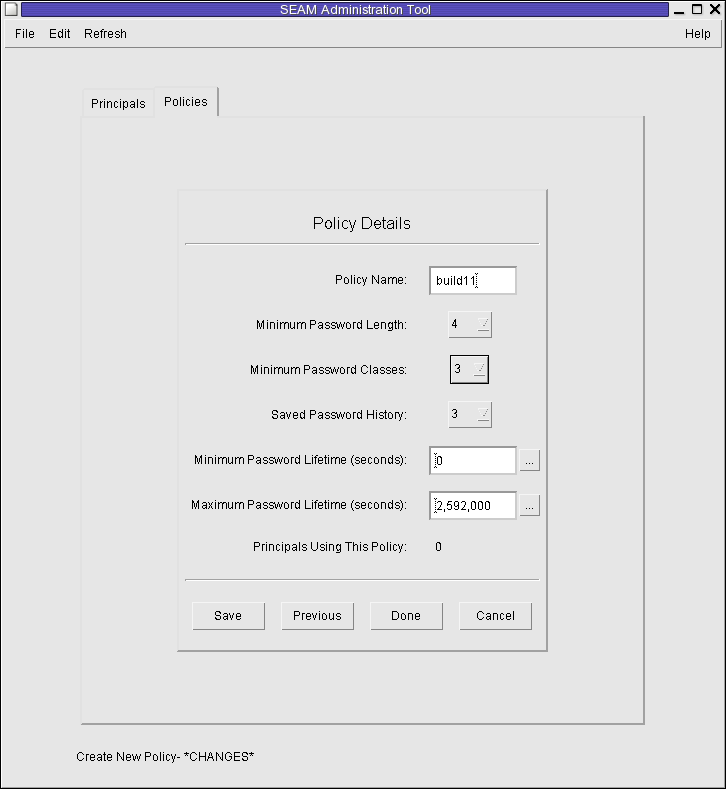
Example 23-12 Creating a New Kerberos Policy
In the following example, a new policy called build11 is created. The Minimum Password Classes is set to 3.
Example 23-13 Creating a New Kerberos Policy (Command Line)
In the following example, the add_policy command of kadmin is used to create the build11 policy. This policy requires at least 3 character classes in a password.
$ kadmin kadmin: add_policy -minclasses 3 build11 kadmin: quit
This procedure explains how to use all or some of the attributes of an existing policy to create a new policy. No command-line equivalent exists for this procedure.
See How to Start the SEAM Tool for more information.
$ /usr/sbin/gkadmin
The Policy Details panel is displayed. All the attributes of the selected policy are duplicated, except for the Policy Name field, which is empty.
The policy name is mandatory. To make an exact duplicate of the policy you selected, skip to Step 6.
Choose Context-Sensitive Help from the Help menu for information about the various attributes in this window. Or, go to Table 23-5 for all the policy attribute descriptions.
An example of the command-line equivalent follows this procedure.
See How to Start the SEAM Tool for details.
$ /usr/sbin/gkadmin
The Policy Details panel is displayed.
Choose Context-Sensitive Help from the Help menu for information about the various attributes in this window. Or, go to Table 23-5 for all the policy attribute descriptions.
Note - You cannot modify a policy's name. To rename a policy, you must duplicate the policy, specify a new name for it, save it, and then delete the old policy.
Example 23-14 Modifying a Kerberos Policy (Command Line)
In the following example, the modify_policy command of kadmin is used to modify the minimum length of a password to five characters for the build11 policy.
$ kadmin kadmin: modify_policy -minlength 5 build11 kadmin: quit
An example of the command-line equivalent follows this procedure.
Note - Before you delete a policy, you must cancel the policy from all principals that are currently using it. To do so, you need to modify the principals' Policy attribute. The policy cannot be deleted if any principal is using it.
See How to Start the SEAM Tool for more information.
$ /usr/sbin/gkadmin
After you confirm the deletion, the policy is deleted.
Example 23-15 Deleting a Kerberos Policy (Command Line)
In the following example, the delete_policy command of the kadmin command is used to delete the build11 policy.
kadmin: delete_policy build11 Are you sure you want to delete the policy "build11"? (yes/no): yes kadmin: quit
Before you delete a policy, you must cancel the policy from all principals that are currently using it. To do so, you need to use the modify_principal -policy command of kadmin on the affected principals. The delete_policy command fails if the policy is in use by a principal.