| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Managing IP Quality of Service in Oracle Solaris 11.1 Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Managing IP Quality of Service in Oracle Solaris 11.1 Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
1. Introducing IPQoS (Overview)
2. Planning for an IPQoS-Enabled Network (Tasks)
General IPQoS Configuration Planning (Task Map)
Planning the Diffserv Network Topology
Hardware Strategies for the Diffserv Network
IPQoS on a Network of Server Farms
Planning the Quality-of-Service Policy
QoS Policy Planning (Task Map)
How to Prepare a Network for IPQoS
How to Define the Classes for Your QoS Policy
How to Define Filters in the QoS Policy
How to Plan Forwarding Behavior
How to Plan for Flow Accounting
3. Creating the IPQoS Configuration File (Tasks)
4. Starting and Maintaining IPQoS (Tasks)
5. Using Flow Accounting and Statistics Gathering (Tasks)
Tasks in the remaining chapters of the guide use the example IPQoS configuration that is introduced in this section. The example shows the differentiated services solution on the public intranet of BigISP, a fictitious service provider. BigISP offers services to large companies that reach BigISP through leased lines. Individuals who dial in from modems can also buy services from BigISP.
The following figure shows the network topology that is used for BigISP's public intranet.
Figure 2-4 IPQoS Example Topology
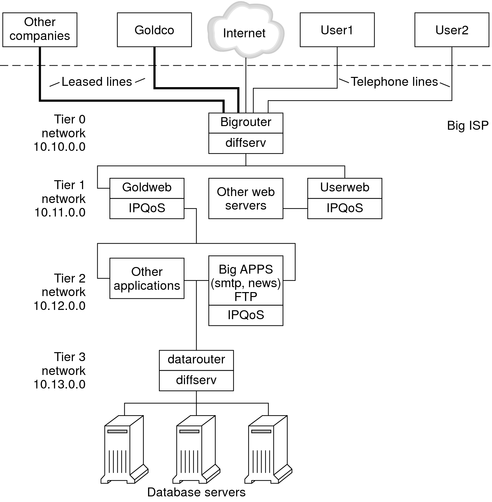
BigISP has implemented these four tiers in its public intranet:
Tier 0 – Network 10.10.0.0 includes a large Diffserv router that is called Bigrouter, which has both external and internal interfaces. Several companies, including a large organization that is called Goldco, have rented leased-line services that terminate at Bigrouter. Tier 0 also handles individual customers who call over telephone lines or ISDN.
Tier 1 – Network 10.11.0.0 provides web services. The Goldweb server hosts the web site which was purchased by Goldco as part of the premium service that Goldco has purchased from BigISP. The server Userweb hosts small web sites that were purchased by individual customers. Both Goldweb and Userweb are IPQoS enabled.
Tier 2 – Network 10.12.0.0 provides applications for all customers to use. BigAPPS, one of the application servers, is IPQoS-enabled. BigAPPS provides SMTP, News, and FTP services.
Tier 3 – Network 10.13.0.0 houses large database servers. Access to Tier 3 is controlled by datarouter, a Diffserv router.