| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Developer's Guide to Oracle Solaris 11 Security Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Developer's Guide to Oracle Solaris 11 Security Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
1. Oracle Solaris Security for Developers (Overview)
2. Developing Privileged Applications
3. Writing PAM Applications and Services
Configuring PAM Through /etc/pam.d
Writing Applications That Use PAM Services
Writing Conversation Functions
Writing Modules That Provide PAM Services
Requirements for PAM Service Providers
Sample PAM Provider Service Module
4. Writing Applications That Use GSS-API
7. Writing Applications That Use SASL
8. Introduction to the Oracle Solaris Cryptographic Framework
9. Writing User-Level Cryptographic Applications
10. Introduction to the Oracle Solaris Key Management Framework
A. Secure Coding Guidelines for Developers
B. Sample C-Based GSS-API Programs
The PAM framework consists of four parts:
PAM consumers
PAM library
The pam.conf(4) configuration file
PAM service modules, also referred to as providers
The framework provides a uniform way for authentication-related activities to take place. This approach enables application developers to use PAM services without having to know the semantics of the policy. Algorithms are centrally supplied. The algorithms can be modified independently of the individual applications. With PAM, administrators can tailor the authentication process to the needs of a particular system without having to change any applications. Adjustments are made through pam.conf, the PAM configuration file or the /etc/pam.d files, which is available from Oracle Solaris 11.1 release onwards.
The following figure illustrates the PAM architecture. Applications communicate with the PAM library through the PAM application programming interface (API). PAM modules communicate with the PAM library through the PAM service provider interface (SPI). Thus, the PAM library enables applications and modules to communicate with each other.
Figure 3-1 PAM Architecture
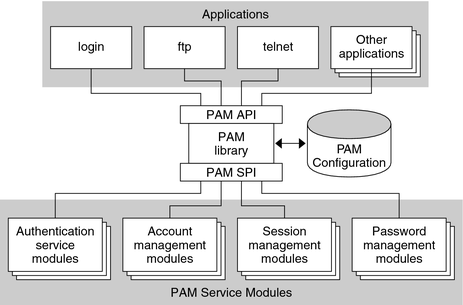
A PAM service module is a shared library that provides authentication and other security services to system entry applications such as login, rlogin, and telnet.
The four types of PAM services are:
Authentication service modules – For granting users access to an account or service. Modules that provide this service authenticate users and set up user credentials.
Account management modules – For determining whether the current user's account is valid. Modules that provide this service can check password or account expiration and time-restricted access.
Session management modules – For setting up and terminating login sessions.
Password management modules – For enforcing password strength rules and performing authentication token updates.
A PAM module can implement one or more of these services. The use of simple modules with well-defined tasks increases configuration flexibility. PAM services should thus be implemented in separate modules. The services can then be used as needed as defined in the PAM configuration. See pam.conf(4).
For example, the Oracle Solaris OS provides the pam_authtok_check(5) module for system administrators to configure the site's password policy. The pam_authtok_check(5) module checks proposed passwords for various strength criteria.
For a complete list of Oracle Solaris PAM modules, see man pages section 5: Standards, Environments, and Macros. The PAM modules have the prefix pam_.
The Oracle Solaris 11.1 release provides a new PAM module pam_user_policy(5) that adds support for per-user PAM configuration. This module calls the pam_eval(3PAM) function to evaluate a named PAM configuration. The pam_eval() routine in the PAM librarylibpam(3LIB), is also new to Oracle Solaris 11.1.
The PAM library, libpam(3LIB), is the central element in the PAM architecture:
libpam exports an API, pam(3PAM). Applications can call this API for authentication, account management, credential establishment, session management, and password changes.
libpam looks for the PAM configuration in /etc/pam.conf or the per-service PAM policy files in /etc/pam.d. The PAM configuration specifies the PAM module requirements for each available service and is managed by a system administrator.
libpam imports an SPI, pam_sm(3PAM), which is exported by the service modules.
As an example of how consumers use the PAM library for user authentication, consider how login authenticates a user:
The login application initiates a PAM session by calling pam_start(3PAM) and by specifying the login service.
The application calls pam_authenticate(3PAM), which is part of the PAM API that is exported by the PAM library, libpam(3LIB).
The PAM library searches for login entries in the PAM configuration corresponding to the service module type of authentication (auth).
For each module in pam.conf that is configured for the login service, the PAM library calls pam_sm_authenticate(3PAM). The pam_sm_authenticate() function is part of the PAM SPI. The pam.conf control flag and results of each call determine whether the user is allowed access to the system. This process is described in more detail in PAM Configuration (Reference) in Oracle Solaris 11.1 Administration: Security Services.
In this way, the PAM library connects PAM applications with the PAM modules that have been configured by the system administrator.
PAM consumers must be linked with the PAM library libpam. Before an application can use any service that is provided by the modules, the application must initialize its instance of the PAM library by calling pam_start(3PAM). The call to pam_start() initializes a handle that must be passed to all subsequent PAM calls. When an application is finished with the PAM services, pam_end() is called to clean up any data that was used by the PAM library.
Communication between the PAM application and the PAM modules takes place through items. For example, the following items are useful for initialization:
PAM_USER – Currently authenticated user
PAM_AUTHTOK – Password
PAM_USER_PROMPT – User name prompt
PAM_TTY – Terminal through which the user communication takes place
PAM_RHOST – Remote host through which user enters the system
PAM_REPOSITORY – Any restrictions on the user account repository
PAM_RESOURCE – Any controls on resources
For a complete list of available items, see pam_set_item(3PAM). Items can be set by the application through pam_set_item(3PAM). Values that have been set by the modules can be retrieved by the application through pam_get_item(3PAM). However, PAM_AUTHTOK and PAM_OLDAUTHTOK cannot be retrieved by the application. The PAM_SERVICE item cannot be set.