| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Trusted Extensions Configuration and Administration Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Trusted Extensions Configuration and Administration Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
Part I Initial Configuration of Trusted Extensions
1. Security Planning for Trusted Extensions
2. Configuration Roadmap for Trusted Extensions
3. Adding the Trusted Extensions Feature to Oracle Solaris (Tasks)
4. Configuring Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
5. Configuring LDAP for Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
Part II Administration of Trusted Extensions
6. Trusted Extensions Administration Concepts
7. Trusted Extensions Administration Tools
8. Security Requirements on a Trusted Extensions System (Overview)
9. Performing Common Tasks in Trusted Extensions
10. Users, Rights, and Roles in Trusted Extensions (Overview)
11. Managing Users, Rights, and Roles in Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
12. Remote Administration in Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
13. Managing Zones in Trusted Extensions
14. Managing and Mounting Files in Trusted Extensions
15. Trusted Networking (Overview)
16. Managing Networks in Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
17. Trusted Extensions and LDAP (Overview)
18. Multilevel Mail in Trusted Extensions (Overview)
19. Managing Labeled Printing (Tasks)
20. Devices in Trusted Extensions (Overview)
21. Managing Devices for Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
22. Trusted Extensions Auditing (Overview)
Trusted Extensions and Auditing
Audit Management by Role in Trusted Extensions
Role Responsibilities for Audit Administration
Audit Tasks in Trusted Extensions
Trusted Extensions Audit Reference
Trusted Extensions Audit Classes
Trusted Extensions Audit Events
Trusted Extensions Audit Tokens
23. Software Management in Trusted Extensions
Creating and Managing a Security Policy
Site Security Policy and Trusted Extensions
Computer Security Recommendations
Physical Security Recommendations
Personnel Security Recommendations
Additional Security References
B. Configuration Checklist for Trusted Extensions
Checklist for Configuring Trusted Extensions
C. Quick Reference to Trusted Extensions Administration
Administrative Interfaces in Trusted Extensions
Oracle Solaris Interfaces Extended by Trusted Extensions
Tighter Security Defaults in Trusted Extensions
Limited Options in Trusted Extensions
D. List of Trusted Extensions Man Pages
Trusted Extensions Man Pages in Alphabetical Order
Oracle Solaris Man Pages That Are Modified by Trusted Extensions
Trusted Extensions software adds audit classes, audit events, audit tokens, and audit policy options to Oracle Solaris. Several auditing commands are extended to handle labels. The following figure shows a typical Trusted Extensions kernel audit record and user-level audit record.
Figure 22-1 Typical Audit Record Structures on a Labeled System
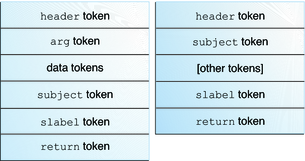
Trusted Extensions adds X windows audit classes to Oracle Solaris. The classes are listed in the /etc/security/audit_class file. For more information about audit classes, see the audit_class(4) man page.
The X server audit events are mapped to these classes according to the following criteria:
xa – This class audits access to the X server, that is, X client connection and X client disconnection.
xc – This class audits server objects for creation or for destruction. For example, this class audits CreateWindow().
xp – This class audits for use of privilege. Privilege use can be successful or unsuccessful. For example, ChangeWindowAttributes() is audited when a client attempts to change the attributes of another client's window. This class also includes administrative routines such as SetAccessControl().
xs – This class audits routines that do not return X error messages to clients on failure when security attributes cause the failure. For example, GetImage() does not return a BadWindow error if it cannot read from a window for lack of privilege.
These events should be selected for audit on success only. When xs events are selected for failure, the audit trail fills with irrelevant records.
xx – This class includes all of the X audit classes.
Trusted Extensions software adds audit events to the system. The new audit events and the audit classes to which the events belong are listed in the /etc/security/audit_event file. The audit event numbers for Trusted Extensions are between 9000 and 10000. For more information about audit events, see the audit_event(4) man page.
The audit tokens that Trusted Extensions software adds to Oracle Solaris are listed alphabetically in the following table. The token definitions are listed in the audit.log(4) man page.
Table 22-1 Trusted Extensions Audit Tokens
|
The label token contains a sensitivity label.
A label token is displayed by the praudit -x command as follows:
<sensitivity_label>ADMIN_LOW</sensitivity_label>
The xatom token identifies an X atom.
An xatom token is displayed by praudit as follows:
X atom,_DT_SAVE_MODE
The xcolormap token contains information about the use of colormaps, including the X server identifier and the creator's user ID.
An xcolormap token is displayed by praudit as follows:
<X_colormap xid="0x08c00005" xcreator-uid="srv"/>
The xcursor token contains information about cursor use, including the X server identifier and the creator's user ID.
An xcursor token is displayed by praudit as follows:
X cursor,0x0f400006,srv
The xfont token contains information about the font use, including the X server identifier and the creator's user ID.
An xfont token is displayed by praudit as follows:
<X_font xid="0x08c00001" xcreator-uid="srv"/>
The xgc token contains information about the graphic context of an X window.
An xgc token is displayed by praudit as follows:
Xgraphic context,0x002f2ca0,srv
<X_graphic_context xid="0x30002804" xcreator-uid="srv"/>
The xpixmap token contains information about the use of pixel mappings, including the X server identifier and the creator's user ID.
An xpixmap token is displayed by praudit -x as follows:
<X_pixmap xid="0x2f002004" xcreator-uid="srv"/>
The xproperty token contains information about various properties of a window, such as the X server identifier, the creator's user ID, and an atom identifier.
An xproperty token is displayed by praudit as follows:
X_property,0x000075d5,root,_MOTIF_DEFAULT_BINDINGS
The xselect token contains the data that is moved between windows. This data is a byte stream with no assumed internal structure and a property string.
An xselect token is displayed by praudit as follows:
X selection,entryfield,halogen
The xwindow token identifies the Xserver and the creator's user ID.
An xwindow token is displayed by praudit as follows:
<X_window xid="0x07400001" xcreator-uid="srv"/>
Trusted Extensions adds two window audit policy options to existing audit policy options.
$ auditconfig -lspolicy ... windata_down Include downgraded window information in audit records windata_up Include upgraded window information in audit records ...
The auditconfig, auditreduce, and auditrecord commands are extended to handle Trusted Extensions information:
The auditconfig command includes the Trusted Extensions audit policies. For details, see the auditconfig(1M) man page.
The auditreduce command adds the -l option for filtering records according to the label. For details, see the auditreduce(1M) man page.
The auditrecord command includes the Trusted Extensions audit events.