| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Managing User Accounts and User Environments in Oracle Solaris 11.1 Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Managing User Accounts and User Environments in Oracle Solaris 11.1 Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
1. Managing User Accounts and User Environments (Overview)
2. Managing User Accounts by Using the Command-Line Interface (Tasks)
3. Managing User Accounts by Using the User Manager GUI (Tasks)
Introducing the User Manager GUI
How to Start the User Manager GUI
Organization of the User Manager Panel
Selecting a Default Name-Service Scope and Type
Adding, Modifying, and Deleting Users and Roles by Using the User Manager GUI
How to Add a User or Role With the User Manager GUI
How to Modify a User or Role With the User Manager GUI
Deleting a User or Role With the User Manager GUI
Administering Advanced Settings With the User Manager GUI
Administering Groups With the User Manager GUI
Administering Roles With the User Manager GUI
How to Administer Roles With the User Manager GUI
Administering Rights Profiles With the User Manager GUI
How to Administer Rights Profiles With the User Manager GUI
Administering Authorizations With the User Manager GUI
The following information is described in this section:
The User Manager GUI is based on the Visual Panels framework and is provided as a Visual Panels interface. The remote management of users and roles is made possible through the Remote Administration Daemon (RAD). The GUI depends on the User/Role Manager RAD module to perform all of its operations. The RAD module works by invoking role-based access control (RBAC) CLIs that perform all of the administrative functions of the GUI.
User authentication and role assumption is provided by the Visual Panels framework itself and is available to all of the panels, including the User Manager panel. The User Manager GUI replaces the Solaris Management Console's User and Roles tool that is supported in Oracle Solaris 10. Although not identical to the Solaris Management Console, the GUI has some of the same functionality. Note that the Solaris Management Console is not supported in this release.
The User Manager GUI presents a simple, clear interface that is easy to use. To minimize the possibility of errors, the GUI presents only those choices that are valid, based on the authorizations and rights profiles of the authenticated user or role. The tasks that can be performed with the GUI are the same as the tasks that you can perform by using the CLI, for example, useradd, usermod, userdel, roleadd, groupadd, and so on. For information about managing users and roles by using the CLI, see Chapter 2, Managing User Accounts by Using the Command-Line Interface (Tasks).
The User Manager GUI is delivered by the pkg:/system/management/visual-panels/panel-usermgr IPS package.
# vp usermgr &
When you Start the User Manager GUI, the main User Manager panel is displayed. The User Manager panel is used to administer users and roles. On the left side of the panel is a Status field that displays the status of the services that are currently running on the local host. On the right of the panel is a User field. The User field displays the credential that is currently being used by the User Manager GUI. To change credentials, click the Lock button on the far right side of the panel. See Assuming a Role or Changing User Credentials.
In the following figure, the main User Manager panel is displayed.
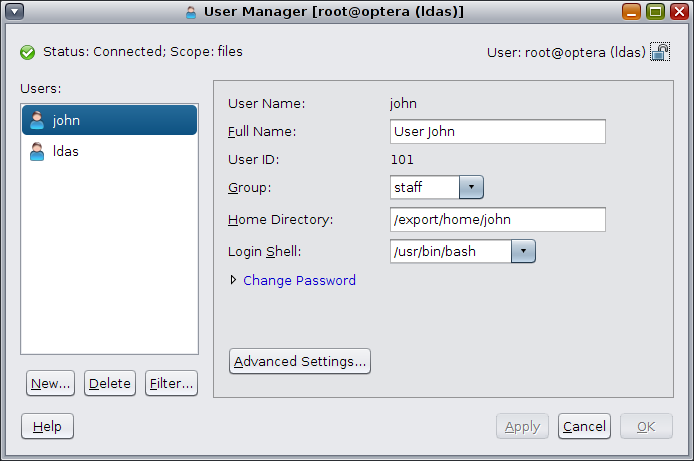
The User Manager panel includes the following components:
Users and Roles list – Contains a list of users from which you can select to administer
Basic Settings – Displays the basic settings for a user, such as user name and full name
To view or modify information for an existing user, select the user from the list of users that is displayed. After you select a user, that user's information is displayed on the right side of the panel.
The following actions are available to you from within the User Manager panel:
Create a new user or role. See How to Add a User or Role With the User Manager GUI.
Delete an existing user or role. See Deleting a User or Role With the User Manager GUI
Filter a user's information. See Selecting a Default Name-Service Scope and Type.
Administer advanced settings for an existing user. See How to Modify a User or Role With the User Manager GUI.
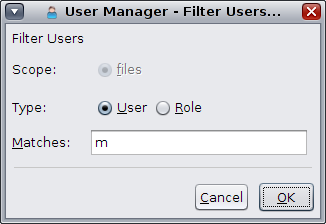
The default name-service scope and type for the User Manager GUI is files and User. To administer the User Manager GUI within a different scope, for example ldap and roles, click the Filter button. Clicking the Filter button launches a dialog box that enables you to change the default scope, type, or both.
Choices for the Scope option are files and ldap.
Choices for Type option are User and Role. Click OK to save the changes.
Click Cancel to cancel the operation.
Note - If the system is not configured as an ldap client, only the files scope is available.
A user with the User Management rights profile can create new users, as long as the advanced attributes of the user or role to be created are a subset of those of the user who is performing the administration. If the user who is performing the administration does not have sufficient authorizations, but has an administrative role with sufficient authorizations, the user can assume that role to perform the necessary administration by clicking the Lock button in the main User Manager panel.
Change Role
Change User
Administer New Host
Clear History
An authentication dialog box is displayed. The authentication dialog box contains a drop-down menu that lists the roles that are available for the specified user.
After assuming the role, you can perform the required administrative tasks.