| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Writing Device Drivers Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Writing Device Drivers Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
Part I Designing Device Drivers for the Oracle Solaris Platform
1. Overview of Oracle Solaris Device Drivers
2. Oracle Solaris Kernel and Device Tree
5. Managing Events and Queueing Tasks
7. Device Access: Programmed I/O
10. Mapping Device and Kernel Memory
13. Hardening Oracle Solaris Drivers
14. Layered Driver Interface (LDI)
Part II Designing Specific Kinds of Device Drivers
15. Drivers for Character Devices
18. SCSI Host Bus Adapter Drivers
Introduction to Host Bus Adapter Drivers
HBA Driver Dependency and Configuration Issues
Entry Points for Module Initialization
_init() Entry Point (SCSI HBA Drivers)
_fini() Entry Point (SCSI HBA Drivers)
Autoconfiguration Entry Points
attach() Entry Point (SCSI HBA Drivers)
detach() Entry Point (SCSI HBA Drivers)
Entry Points for SCSA HBA Drivers
Target Driver Instance Initialization
Allocation and Initialization of a scsi_pkt(9S) Structure
Reallocation of DMA Resources for Data Transfer
tran_destroy_pkt() Entry Point
Interrupt Handler and Command Completion
tran_reset_notify() Entry Point
SCSI HBA Driver Specific Issues
x86 Target Driver Configuration Properties
19. Drivers for Network Devices
Part III Building a Device Driver
22. Compiling, Loading, Packaging, and Testing Drivers
23. Debugging, Testing, and Tuning Device Drivers
24. Recommended Coding Practices
B. Summary of Oracle Solaris DDI/DKI Services
C. Making a Device Driver 64-Bit Ready
SCSA is the DDI/DKI programming interface for the transmission of SCSI commands from a target driver to a host adapter driver. By conforming to the SCSA, the target driver can easily pass any combination of SCSI commands and sequences to a target device. Knowledge of the hardware implementation of the host adapter is not necessary. Conceptually, SCSA separates the building of a SCSI command from the transporting of the command with data to the SCSI bus. SCSA manages the connections between the target and HBA drivers through an HBA transport layer, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 18-1 SCSA Interface
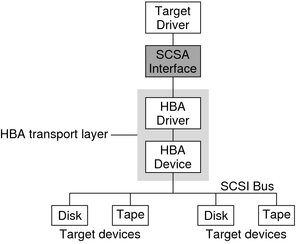
The HBA transport layer is a software and hardware layer that is responsible for transporting a SCSI command to a SCSI target device. The HBA driver provides resource allocation, DMA management, and transport services in response to requests made by SCSI target drivers through SCSA. The host adapter driver also manages the host adapter hardware and the SCSI protocols necessary to perform the commands. When a command has been completed, the HBA driver calls the target driver's SCSI pkt command completion routine.
The following example illustrates this flow, with emphasis on the transfer of information from target drivers to SCSA to HBA drivers. The figure also shows typical transport entry points and function calls.
Figure 18-2 Transport Layer Flow