| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Solaris 11 Desktop Accessibility Guide Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Solaris 11 Desktop Accessibility Guide Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
1. Introduction to Accessibility
2. Using Assistive Technologies
Orca Screen Reader and Magnifier
Enabling General Preferences in Orca
Quit Orca Without Confirmation
Enabling Speech Preferences in Orca
Speech System and Speech Synthesizer
Speak Multicase Strings as Words
Break Speech Into Chunks Between Pauses
To Speak Indentation and Justification
Enabling Braille Preferences in Orca
Enabling Key Echo Preferences in Orca
Enabling Magnifier Preferences in Orca
Tracking and Alignment Settings
Enabling Key Bindings Preferences in Orca
Enabling Pronunciation Preferences in Orca
Using the Orca Keyboard Commands
Using the Desktop Layout Commands
Using the Laptop Layout Commands
Miscellaneous Keyboard Commands
Application-Specific Information
To Change the PDF Viewer Application
3. Configuring the Mouse and Keyboard
4. Using the Keyboard to Navigate the Desktop
Orca is a flexible and powerful assistive technology for people with visual impairments. Using various combinations of speech synthesis, Braille, and magnification, Orca provides access to applications and toolkits that support the Assistive Technology Service Provider Interface (AT-SPI). Orca is free, open-source software.
The Orca Screen Reader and Magnifier applications help users with limited or no vision to use the Oracle Solaris Desktop and its associated applications. Orca provides the following functionalities:
Screen Reader – Enables non-visual access to standard applications in the Oracle Solaris Desktop by using speech and Braille output
Magnifier – Enables automated focus tracking and full-screen magnification to aid low-vision users
Orca is a part of the GNOME platform and its releases are coupled with the GNOME platform releases.
The following sections provide information about Orca and how to use it.
Braille is supported through BRLTTY and is tightly integrated with Orca. BRLTTY offers support for nearly every refreshable Braille.
Also, Orca fully supports contracted Braille output.
Orca provides interfaces to both gnome-speech and emacspeak speech services. Currently available voices for Orca are restricted by the speech engines supported by the available speech services.
Some of the following speech engines are available:
Free engines:
eSpeak
Festival
FreeTTS
Commercial engines:
Fonix DECtalk
Loquendo
Eloquence
Cepstral
Orca currently uses the gnome-mag magnification service. The gnome-mag service has incorporated support for smoother full-screen magnification, which relies upon newer extensions in the X Window System server. These extensions do not always function well on all platforms, so smooth full-screen magnification might not always work.
This procedure describes how to enable Orca for the first time. Press Return after each action to proceed through the setup.
You can change the settings at any time by running the --text-setup option when you start Orca, or by pressing Insert+Spacebar while Orca is running to start the Orca Configuration GUI. The settings are saved in the ~/.orca/user-settings.py file. You need to log out and log back in for the new settings to take effect.
orca --text-setup Enter
The default language is set to English.
Note - Using the default eSpeak text-to-speech engine, Orca supports about 45 languages.
The options are:
1 – Desktop uses the Insert key
2 – Laptop uses the Caps Lock key
This functionality assumes that a BRLTTY compatible device is available, although Orca can still function if you type y without a BRLTTY device available.
This feature is useful for developers who need to verify BRLTTY output, but may also be useful in other situations, such as visually diagnosing or verifying Braille output.
Orca should be enabled on your system.
Note - If accessibility was not yet enabled, Orca enables accessibility and then advises you to log out and restart your login session.
If you plan to use the Magnifier portion of Orca in full screen mode, confirm that the Xserver Composite extension is enabled. To enable the Xserver Composite extension, perform the following actions:
Press Alt+F2 or Meta+R to open the Run dialog.
Type the xdpyinfo command and press Enter.
Look for the string Composite in the output.
This section describes the usage of Orca.
When you run Orca for the first time, the application automatically opens in setup mode. If you want to run setup at a later point, execute the --setup option the next time you run Orca. While Orca is running, you can press Insert+Spacebar to open the Orca Configuration GUI.
Orca's Configuration GUI also has an option to let you indicate that Orca should be started automatically when you log in. For more information about the Orca's graphical user interface, see Orca Configuration GUI.
Run Orca by typing the orca command in a terminal session window.
You can run Orca from a virtual console window if you do not yet have access to the GUI.
If the GUI is installed, press Alt+F2 or Meta+R. In the Run dialog, type orca (followed by any of the optional parameters) and press Return.
Orca automatically enters the text setup mode if you run it from a virtual console window.
Press Insert+Q in the desktop mode or CapsLock+Q in the laptop layout mode, to quit Orca.
A confirmation dialog appears.
Select Quit to close Orca.
If the system does not respond, you can perform any one of the following:
Press Ctrl+Alt+F1 to get to a virtual console and enter orca --quit command. Then, press Alt+F7 to get back to the desktop. This procedure kills the Orca process and reclaims system resources. You can then restart Orca by using the previously outlined methods.
Press Ctrl+Alt+Backspace to end your login session and get back to the graphical login prompt.
The Orca Configuration GUI enables you to customize the behavior and features of Orca, such as speech, Braille, and magnification. For example, you can select the type of speech synthesis engine you want to use, enable or disable Braille, and the type of magnification preferences you want to set. You can select the keyboard layout you want (desktop or laptop) and also examine and modify the existing keyboard layout.
To open the Orca Configuration GUI, press Orca Modifier+Spacebar, where Orca Modifier is the Insert key when you use the Desktop keyboard layout and CapsLock key when you use the Laptop keyboard layout. To change settings for a single application, press Ctrl+Orca Modifier+ Spacebar while the application has focus.
For more information about the Desktop keyboard layout, see Using the Desktop Layout Commands.
For more information about the Laptop keyboard layout, see Using the Laptop Layout Commands.
The General page enables you to customize general settings of Orca such as selecting the keyboard layout and starting and quitting Orca. The options in the General page are described in the following sections.
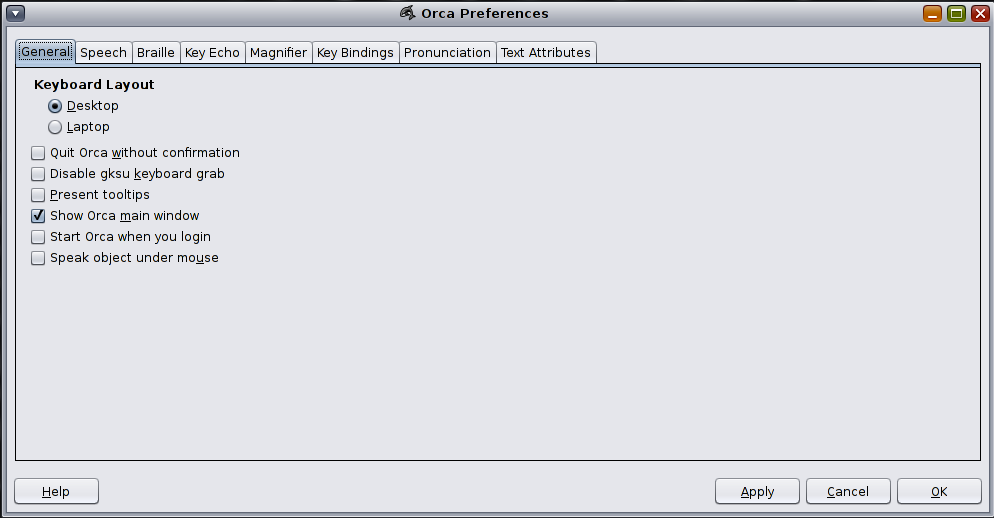
The keyboard layout section enables you to select the Desktop or Laptop layout.
For more information about the Desktop keyboard layout, see Using the Desktop Layout Commands.
For more information about the Laptop keyboard layout, see Using the Laptop Layout Commands.
The Orca main window enables you to display the Orca Configuration GUI.
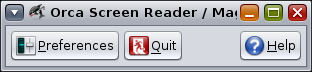
The main window provides a Quit option to close the Orca Configuration GUI. You can also quit Orca by pressing Orca Modifier+Q. Because the Orca main window is included in the window manager's tab order when you press Alt+Tab to switch windows, you might want to deselect the Show Orca main window button.
When you press Orca Modifier+K to quit Orca or press the Quit button in the Orca main window, Orca displays a confirmation dialog asking whether you want to quit. Select this option to prevent the confirmation window from appearing again.
When running commands from the Launch menu, many distributions use an application known as gksu to authorize the user to run these commands. gksu is the GUI which asks you for your password. When gksu runs, the application enables the keyboard grab feature.
Keyboard grab is a feature to prevent keyboard actions from going to any other application on the desktop, including Orca. The result of a keyboard grab is that Orca will not receive any keyboard events, preventing it from functioning normally.
By selecting the Disable gksu Keyboard Grab button, you can turn off the keyboard grab behavior, allowing Orca to function normally with system administration applications.
Note - The keyboard grab is a security attempt by gksu to prevent applications from sniffing the keyboard and grabbing secret information. Disabling the gksu keyboard grab feature can expose you to such behavior. You can use the root account for system administration purposes. To do this for system administration purposes, you need to enable the root account for login, and then logout and log back in as root whenever you want to perform a system administration command.
The Present tooltips option displays information in tooltips that appear as the result of mouse hovering. Pressing Ctrl+F1 when an object has focus always displays tooltips regardless of this setting.
When the Speak Object Under Mouse option is selected, Orca presents audio information about the object under the mouse.
When the Start Orca When You Login option is selected, the system automatically launches Orca when you log in.
The Speech page enables you to customize the Orca speech synthesis settings.
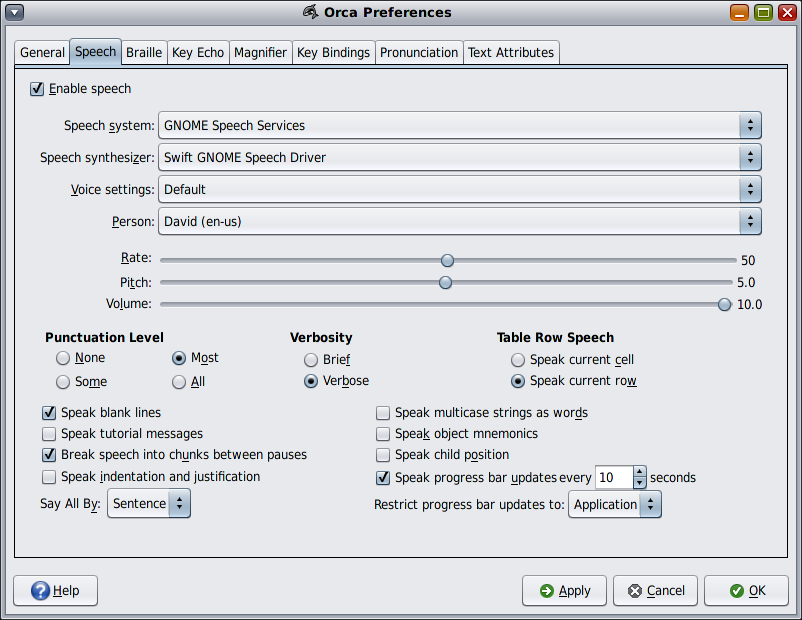
The Enable Speech option causes Orca to make use of a speech synthesizer.
These options enable you to select the speech system and synthesizer. Orca provides support for a growing number of speech systems. These include GNOME-speech, Emacspeak, and an experimental backend for Speech Dispatcher. Depending on the machine configurations, you might have all or none of these options. By default, only GNOME-speech is available.
First, determine which speech system you would like to use. Then, choose from the Speech Synthesizer list of available synthesizers.
If your synthesizer supports voice settings, Orca can use multiple voices to identify special cases within an application, such as hyperlinks or uppercase text. Use the Voice Settings and Person options to customize these settings. For example, assume you are using Fonix DECtalk and want the Betty voice to denote uppercase. Do the following:
Select the uppercase voice for the Voice Settings option.
For the Person option, select the Betty voice.
Use the next sliders to set the synthesizer's rate, pitch, and volume.
Use the Punctuation Level setting to adjust the amount of punctuation spoken by the synthesizer. The following levels are available:
None
Some
Most
All
The Verbosity setting determines the amount of information that is spoken in certain situations. For example, if the Verbose level is set, the synthesizer speaks shortcut keys for items in menus. When it is set to Brief, these shortcut keys are not announced.
The Table Row Speech option determines the way the speech synthesizer will read items within tables. The following settings are available:
Speak Current Row
Speak Current Cell
The ability to adjust this behavior can be useful in many situations. For example, consider the process of browsing email messages in Evolution. In this instance, the Speak current row setting is preferable. While navigating through the list of messages, all relevant info, such as the sender, subject, and whether the message has attachments, is read automatically. While the current row setting is active, you can still read individual cells by using the left and right arrows.
Note - To toggle this behavior, press Orca Modifier+F11.
To hear the word blank when navigating to a blank line in a document, select the Speak Blank Lines option.
The Speak Multicase Strings As Words option causes Orca to break a word prior to passing it along to the speech synthesizer. So words in code, consisting of several words with alternating case are pronounced correctly.
For example, the word “MultiCaseString” can be broken into separate words Multi, Case, and String.
If the Speak Tutorial Messages option is selected, when moving from one component to another in an interface, Orca provides information about the component that is currently focused.
The Speak Object Mnemonics option causes Orca to announce the mnemonic associated with the object in focus. For example, Alt+O for the OK button.
Depending on the enabled speech settings, Orca might provide some information about a particular object such as its name, role, state, mnemonic, and tutorial message. The Break Speech Into Chunks Between Pauses option causes Orca to insert brief pauses in between each piece of information.
The Speak Child Position checkbox enables Orca to announce the position of the focused item in menus and lists. For example, 9 of 16.
The Speak Indentation And Justification option causes Orca to provide justification and indentation information.
If the Speak Progress Bar Updates setting is enabled, Orca periodically announces the status of progress bars. How often the announcement is made is determined by the value chosen as the Update interval spin. This setting is only available if the Speak Progress Bar Updates option is selected.
Use the Restrict Progress Bar Updates setting to control which progress bars should be spoken. The default value is Application. The following choices are available:
All – Orca speaks updates for all progress bars regardless of where they are located
Application – Orca speaks updates from progress bars in the active application even if they are not in the active window
Window – Orca only speaks updates only for progress bars in the active window
The Say All By setting specifies whether the Say All functionality of Orca speaks by sentence or line.
The Braille page enables you to customize various aspects about the use of Braille.
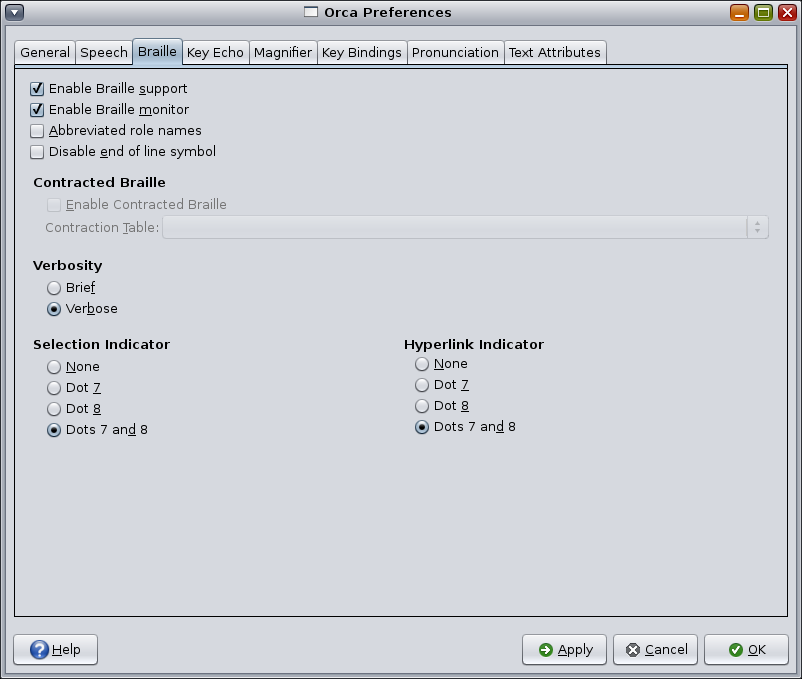
Note - Orca does not automatically start BRLTTY for you. You need to do this at boot time.
Select the Enable Braille Support option to make use of a Braille display. By default, this option is enabled.
If BRLTTY is not running, Orca recovers gracefully and does not communicate with the Braille display. If you configure BRLTTY later, you need to restart Orca to use Braille.
Orca's Braille monitor provides an on-screen representation of what takes place on the Braille display. This feature is mostly for demonstration purposes, but is also useful for Orca developers who do not have access to a Braille display.
The Abbreviated Role Names check box determines the manner in which role names are displayed and can be used to help conserve real estate on the Braille display. For example, if a slider had focus and the Abbreviated Role Names option is selected, the word “slider” is abbreviated to “sldr”.
The Disable end of line symbol option tells Orca to not present the $l string at the end of a line.
Orca supports contracted Braille through the Liblouis project. Refer to the Orca wiki to find additional information about setting up Liblouis with Orca.
The Verbosity options determine the amount of information that will be displayed in Braille in certain situations. For example, if the option is set to Verbose, keyboard shortcut and role name information is displayed. This information is not displayed in Brief mode.
When you select text, Orca underlines the text on your Braille display with dots 7 and 8. If you prefer, you can change the indicator to Dot 7 or Dot 8, or not provide an indicator.
When you encounter a hyperlink, Orca underlines that text on your Braille display with dots 7 and 8. If you prefer, you can change the indicator to Dot 7 or Dot 8, or not provide an indicator.
The Key Echo page enables you to specify the behavior of Orca when pressing keys on the page and whether words are spoken as you complete them.
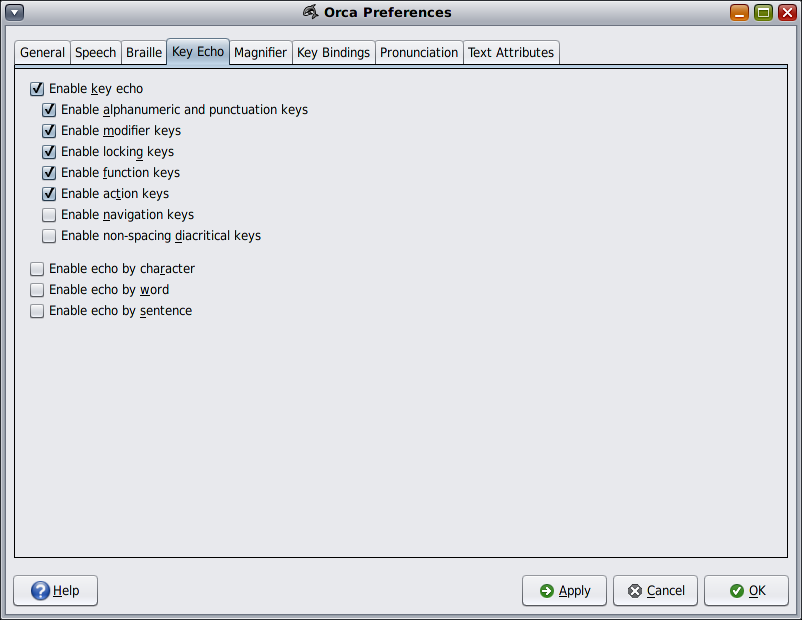
The key echo feature offers increased flexibility. For example, one user might choose to enable all the key echo options, while another might prefer to use word echo, but only have locking keys announced.
The Enable Key Echo option provides specific settings for the key echo feature:
Enable Alphanumeric And Punctuation Keys – Includes all alphabetical, numeric, and punctuation keys.
Enable Modifier Keys – Includes Shift, Ctrl, and Alt keys.
Enable Locking Keys – Includes Caps Lock, Scroll Lock, and Num Lock keys.
Enable Function Keys – Includes function key groups.
Enable Action Keys – Consists of keys that perform some logical action, such as Backspace, Return, and Tab.
Enable Navigation Keys – Includes the four arrow keys as well as any key combination in which the Orca Modifier key is being held down. The latter is designed to prevent Orca from echoing flat review commands.
Enable Non-spacing Diacritical Keys – These are the non printing keys that are used to generate accented letters.
The Enable Echo by Character option causes an echo of the characters you just typed. While echo by character seems similar to the key echo of alphanumeric and punctuation keys, there are important differences related to accented letters and other symbols for which there are no dedicated keys. Key echo announces the key that is just pressed and character echo announces the characters that was just inserted.
The Echo by Character option is always available, regardless of whether any of the other key echo options are selected.
The Enable Echo by Word option causes an echo of the word you just typed. The Echo by Word option is always available, regardless of whether any of the key echo options are selected.
The Enable Echo by Sentence option causes an echo of the sentence you just typed. The Enable Echo by Sentence control is always available regardless of whether any of the other key echo options are selected.
The Magnifier page enables you to enable or disable magnification and specify how magnification must be performed.
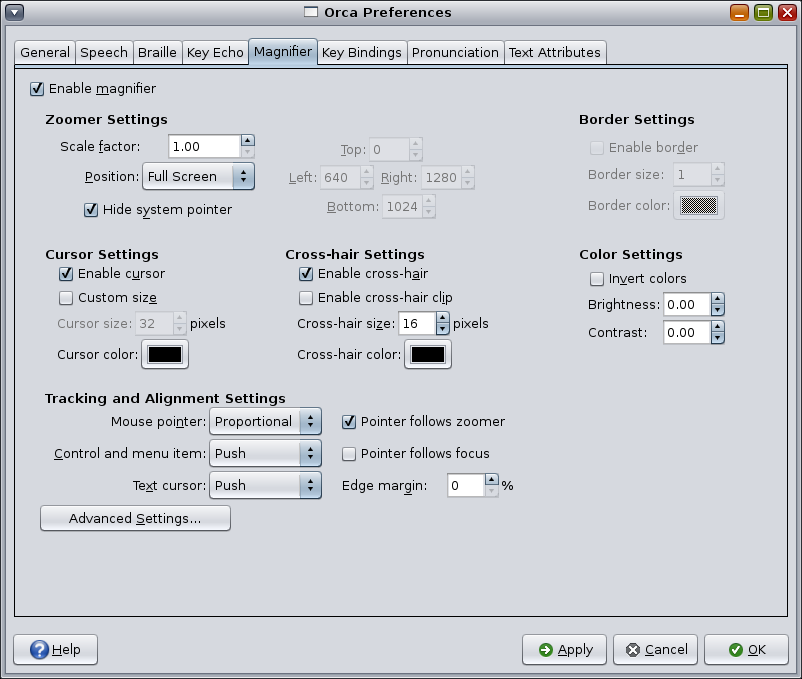
The Enable Magnifier option causes Orca to provide magnification.
Two zoomer GUI controls determine magnification characteristics:
Scale Factor – Sets the magnification power from 1.0x to 16.0x. Fractional values are supported.
Position – Sets the location and size of the magnifier window, and provides the following options:
Full Screen
Left Half
Right Half
Top Half
Bottom Half
Custom
The default position is Full Screen. The Custom setting enables you to define the location of each edge of the zoom window. Units are in pixels.
The Enable Border option determines whether a window border is visible for the magnifier. The Border Size option determines the size of the border in pixels.
Note - These options are not available in Full Screen mode.
You can use Cursor Settings to customize the size and color of the magnifier's cursor by using the following options:
Enable Cursor – If enabled, a cursor is visible and the size and color options are available.
Custom Size – If enabled, the mouse pointer appears larger than the normal size. The cursor size can be changed from the default value of 32 pixels.
Custom Color – If enabled, you can apply a custom.
You can use Cross-hair Settings to customize the magnifier's optional area-targeting cursor by using the following options:
Enable Cross-hair – If selected, you can configure the clipping behavior, size, and color of the cross-hair.
Enable Cross-hair Clip – If selected, the cross-hair is clipped (removed) in the area immediately surrounding the mouse pointer.
Cross-hair Size – Sets the thickness of the cross-hair in pixels.
Cross-hair Color – Enables you to apply a custom color.
Color Settings enables you to adjust the color of the magnified region by using the following options:
Invert Colors – Creates a reverse or a negative-image effect.
Brightness – Ranges from -1 (black or no brightness) to 1 (white or total brightness). 0 is normal or unchanged.
Contrast – Ranges from -1 (grey or no contrast) to 1 (1 is maximum contrast). 0 is normal or unchanged).
Tracking and Alignment Settings control the tracking of the mouse cursor. The following tracking and alignment settings options are available:
Mouse Pointer – Choose from the following options:
Centered – Keeps the mouse pointer at the center of the screen whenever possible. This is the default option.
Proportional – Positions the mouse pointer in the zoom window relative to its actual, unmagnified position. For instance, if the mouse pointer is 25% away from the left edge of the desktop, Orca positions the magnified mouse pointer 25% from the left edge of the zoom window.
Push – Moves the zoomer window to the least amount necessary to keep the mouse pointer on the screen.
None – Moving the mouse pointer has no impact on what the zoomer window displays.
Pointer Follows Zoomer – This option is enabled by default. If the mouse pointer is not on the screen when you initially move the mouse, it is moved into the zoomer so that you can continue to see what you were working on. If your preferred mouse tracking mode is centered, the pointer is moved to the center; otherwise, it is moved to the item with focus.
Control And Menu Item – These options control additional behavior of the magnifier.
Centered – When navigating using the keyboard, keep the focused dialog box control or menu item at the center of the screen whenever possible.
Push – When navigating using the keyboard, move the zoomer window to the least amount necessary to display the focused dialog box control or menu item. This is the default option.
None – Using the keyboard to navigate among dialog box controls and menu items will have no impact on what the zoomer window displays.
Pointer Follows Focus – If this option is enabled, the mouse pointer follows you as you navigate through menu items and move among controls in dialog boxes. This option is disabled by default.
Text Cursor – These options control how the text cursor behaves.
Centered – As the text cursor moves, keep the cursor at the center of the screen whenever possible.
Push – As the text cursor moves, move the zoomer window to the least amount necessary to display it. This is the default option.
None – Moving the text cursor does not affect what the zoomer window displays.
Edge Margin – The edge margin determines how close the caret should be allowed to get to the edge of the screen before the zoomer window is pushed. The margin can range from 0 to 50%, with 50% being the equivalent of choosing centering. The default value is 0.
Note - This option is only available if Push is your text cursor tracking mode.
Advanced Settings – Clicking the Advanced Settings button located near the bottom of the Magnifier page displays the Advanced Settings dialog.
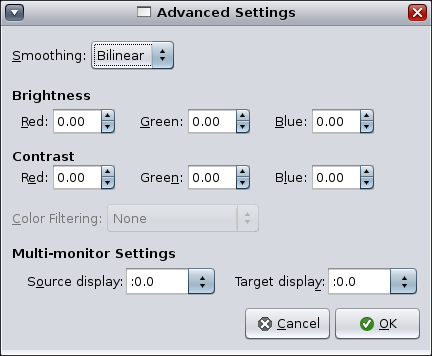
You can set the following options:
Smoothing – Bilinear or none.
Brightness – Red, Green, Blue: Individual controls for choosing different brightness levels for each color.
Contrast – Red, Green, Blue: Individual controls for choosing customized contrast levels. These settings are not as significant as changes to brightness.
Color Filtering – Enables you to pick one of the color blind filters available through libcolorblind.
Note - To take advantage of this feature, you need to install libcolorblind and then rebuild gnome-mag.
Multi-Monitor Settings - Source Display X Window System DISPLAY of what should be magnified. Written in the form :0.n where n is the number of the screen whose contents should be magnified.
Multi-Monitor Settings - Target Display X Window System DISPLAY of where to put the zoomer window. Written in the form :0.n where n is the number of the screen where the zoomer window should appear.
The Key Bindings page enables you to examine and modify the key bindings for Orca.
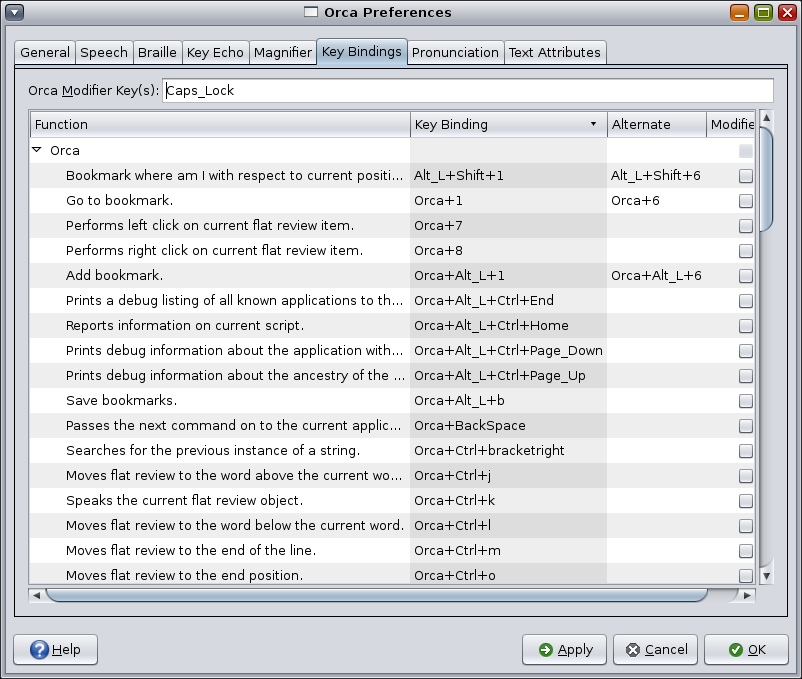
The first control on the Key Bindings window enables you to determine which key or keys act as the Orca modifier. The Orca Modifier is the key that you press and hold in conjunction with other keys to give commands to Orca.
For desktop keyboards, the default Orca Modifier is the Insert key. For laptop keyboards, the default Orca Modifier is the Caps Lock key. See the Desktop keyboard layout and Laptop keyboard layout sections for the default values.
Note - You cannot modify the Orca modifier key by using the Configuration GUI.
The Key Bindings table provides a list of Orca operations and keys that are bound to them.
The Function column header provides the description of the Orca operation to be performed.
The Key Binding header is the primary way to invoke the function from the keyboard. If the function description includes the word "Orca", the Orca Modifier key should be held down along with the other indicated keys.
The Alternate header provides an alternate mechanism for invoking the function from the keyboard.
To modify either the Key Binding or the Alternate bindings, navigate to the cell and press Return. Then, press a key combination and press Return to confirm the new combination. The new keystroke is saved and the check box in the last column (the Modified column) indicates that the key binding has been modified.
To undo a modified keybinding, navigate to the modified column, deselect the checkbox, and click the Apply button, Alt+A.
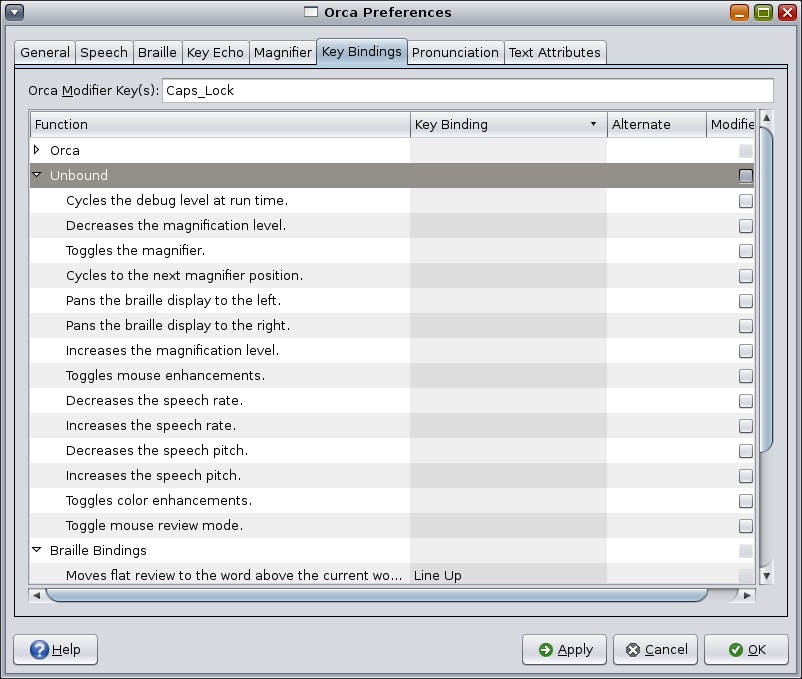
Beneath the list of Orca keybindings, is a group of unbound commands. These commands are useful for some users but not needed by most users. Rather than appropriating a keystroke for such commands, these keys are unassigned.
You can assign a keystroke to any of these unbound commands as follows:
Press Return to edit the keybinding.
Press Delete or Backspace when prompted for the new keybinding.
Press Return to confirm.
Sometimes your speech synthesizer might not correctly use words to convey or pronounce a particular string. For example, you might prefer to hear "laughing out loud" rather than "LOL," or a name or a technical term the synthesizer might mispronounce. On the pronunciation page, you can add, edit, and delete Orca's pronunciation dictionary entries. The pronunciation page is part of the Application-specific Settings dialog that is started when you give a particular application focus and type Orca Modifier+Ctrl+Spacebar. You can therefore customize your entries as you need for each application that you use.
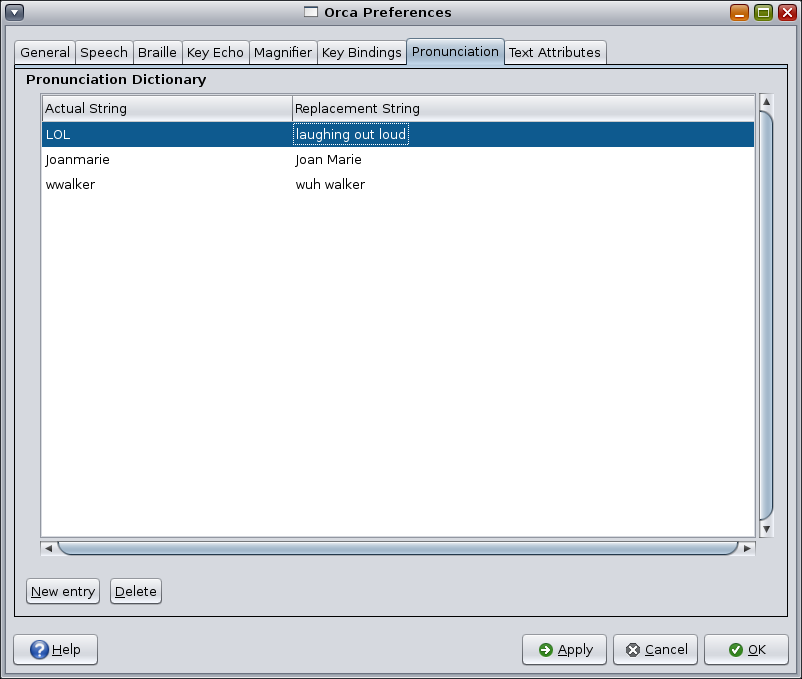
Orca speaks known text attribute information about an object when you press Orca Modifier. The Text Attributes page of the configuration GUI enables you to customize the text attributes that Orca will present.
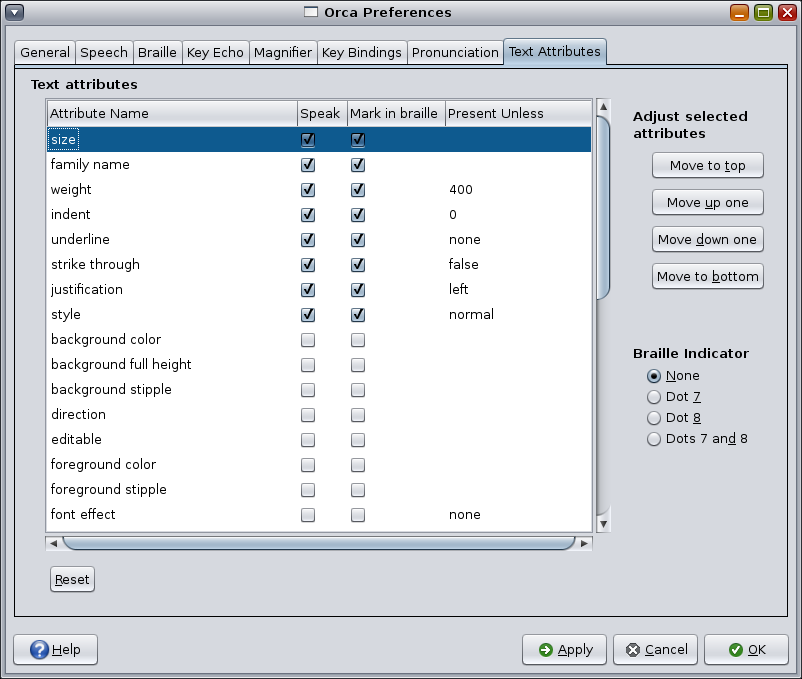
This page displays a text attribute list, where each row consists of four columns:
The name of the text attribute.
A checkbox that indicates whether this text attribute should be spoken.
A checkbox that indicates whether this text attribute should be underlined on the Braille display.
An editable Present unless string value. The value of the attribute will only be presented if it is not this value.
For example, by default, the underline text attribute has a value of none. If this attribute is selected and the user types Orca Modifier+F, and the text in question is not underlined, then this attribute is not spoken. If you always want this attribute to be spoken regardless of whether the text is underlined, select the attribute and clear the Present unless value.
Use the Reset button (Alt+R) to set the list values back to their initial state when the dialog is first displayed.
When you initially display the text attribute pane, all the selected attributes are displayed at the top of the list. They are given in the order that they will be spoken and used in Braille.
To select others or adjust the order, use the Adjust Selected Attributes buttons:
Move to top (Alt+T) — Moves the selected attribute to the top of the list.
Move up one (Alt+U) — Moves the selected attribute up one row.
Move down one (Alt+D) — Moves the selected attribute down one row.
Move to bottom (Alt+B) — Moves the selected attribute to the bottom of the list.
Use the Braille Indicator buttons to select the cell or cells to be used to indicate text which has at least one of the specified attributes. The choices are:
None (default)
Dot 7
Dot 8
Dots 7 and 8
Text attributes can also be set on an individual application basis. The Text Attribute pane is also part of the Application-specific Settings dialog box that is started when you give a particular application focus and type Orca Modifier+Ctrl+Spacebar.
The Key Bindings page provides a complete list of the available keyboard commands of the Orca Configuration GUI. To open the Orca Configuration GUI, press Orca Modifier+Spacebar.
To enter Orca's Learn mode while running Orca, press Orca Modifier+H. When in Learn mode, Orca will intercept all keyboard and Braille input events and indicate what the effect would be. To exit Learn mode, press the Escape key.
Orca provides additional commands for some applications, such as Firefox. To display the list of additional commands for an application, press Ctrl+Orca Modifier+Spacebar when that application has focus. The Orca Configuration GUI opens in the application-specific state, and additional commands appear in the Key Bindings page.
The GNOME Desktop also has built in keyboard commands to control the desktop and its applications. For more information about the GNOME shortcut keys, see Chapter 4, Using the Keyboard to Navigate the Desktop
 | Caution - The MouseKeys use the KP_Insert key to emulate a mouse button press. When enabled, MouseKeys can conflict with KP_Insert as the Orca modifier, resulting in a stuck Orca modifier key. As an alternative, you can use the laptop key bindings, which avoid the keypad for Orca commands. If you accidentally enable MouseKeys, you can disable it using the gnome-keyboard-properties application. |
The following sections list the common Orca keyboard commands for desktop keyboards arranged by category.
The following table lists the keyboard shortcuts for the flat review commands when you use the desktop layout.
|
Note - These commands apply when working with objects as well as when working with text. For example, if the flat review cursor is positioned on a menubar, issuing the “read current line” command would speak the names of all visible menus. Similarly, issuing the “read next word” command would speak the object to the right of the flat review cursor on the same line, or move flat review to the next line if no more objects were found.
The following table lists the shortcut keys for the bookmark commands when you use the desktop layout.
|
The following table lists the shortcut keys for miscellaneous functions when you use the desktop layout.
|
The following table lists the shortcut keys for the debugging commands when you use the desktop layout.
|
Following is a list of common Orca keyboard commands for laptop keyboards arranged by category.
The following table lists the keyboard shortcuts for the flat review commands when you use the Laptop layout.
|
These commands apply when working with objects as well as when working with text. For example, if the flat review cursor is positioned on a menubar, issuing the “read current line” command speaks the names of all visible menus. Similarly, issuing the “read next word” command speaks the object to the right of the flat review cursor on the same line, or move flat review to the next line if no more objects were found.
The following table lists the keyboard shortcuts for the bookmark commands when you use the laptop layout.
|
The following table lists the shortcut keys for the miscellaneous functions when you use the Laptop layout.
|
The following table lists the shortcut keys for the debugging commands when you use the Laptop layout.
|
Orca is designed to work with applications and toolkits that support the Assistive Technology Service Provider Interface (AT-SPI). These applications include the Oracle Solaris Desktop and its bundled applications: OpenOffice, Firefox, and the Java platform.
A tabbed dialog window similar to the Orca Configuration dialog is displayed with the following differences:
No initial General pane.
The Speech System and Speech Synthesizer options on the Speech pane are inactive.
Any application-specific key bindings appear at the top of the list on the Key Bindings pane.
A new application-specific settings pane might appear at the end of the standard set of tabs. Press the End key from the tab list to go directly to the right-most tab.
Adjust your application-specific settings. For example, you might have Key Echo disabled generally in Orca but would like to specifically have it enabled for the GNOME Calculator application.
When you have customized your application settings, click OK.
These settings are written to your ~/.orca/app-settings directory in a file called APPNAME.py, where APPNAME is the name of the application.
Orca automatically writes these files. The contents of the file are overwritten each time you change your application settings for that application.
To retain any application-specific settings or code, copy them to a file called ~/.orca/app-settings/APPNAME-customizations.py. This file is automatically read when the settings for the application are loaded.
Note - If you adjust one or more application-specific key bindings, the new values will not take effect until you click OK. The workaround is to either restart Orca, or to press Alt+Tab to move to another application and then press Alt+Tab to return to the application for which you have just changed the key bindings.
Orca uses BRLTTY for Braille support. BRLTTY is used to access the text mode console content. On a typical Braille-enabled installation of Oracle Solaris, BRLTTY is already running and provides access to text consoles. When Orca starts, it connects to BRLTTY. If you switch from a text console to your X Windows session, your Braille display automatically follows and displays the content that Orca is presenting to you.
Orca currently works best with BRLTTY v3.8 or greater and also works well with BRLTTY v3.7.2. This document provides information about using Orca with BRLTTY 3.8.
This section describes troubleshooting topics in Orca.
Press Alt+F2 or Meta+R to open the Run dialog.
Type orca and press Return to start a new instance of Orca.
This will force any existing Orca processes to exit and then restart Orca.
Sometimes, this step might cause the desktop to hang, which is usually because of an ill-behaved application.
Note - If you cannot get to a terminal window, try pressing Ctrl+Alt+Backspace, which shuts down the X Window System server.
This action should return you to the login screen.